This article explains how does generator work. Power generators, also known as gensets, deliver reliable electricity whenever the main power grid fails. They serve as backup power sources for homes, businesses, and worksites, ensuring that essential systems remain operational during blackouts or emergencies. So, how exactly do generators produce electricity?
How Does a Generator Work
In simple terms, a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process relies on an engine, alternator, and fuel system. The science behind it is electromagnetic induction—a principle discovered by Michael Faraday—which states that electricity is generated when a conductor moves within a magnetic field.
In addition to understanding the process, learning about how generators work would allow you to select the right generator for your specific needs, ensure optimal performance, and maintain long-term reliability.
Main Components of a Generator
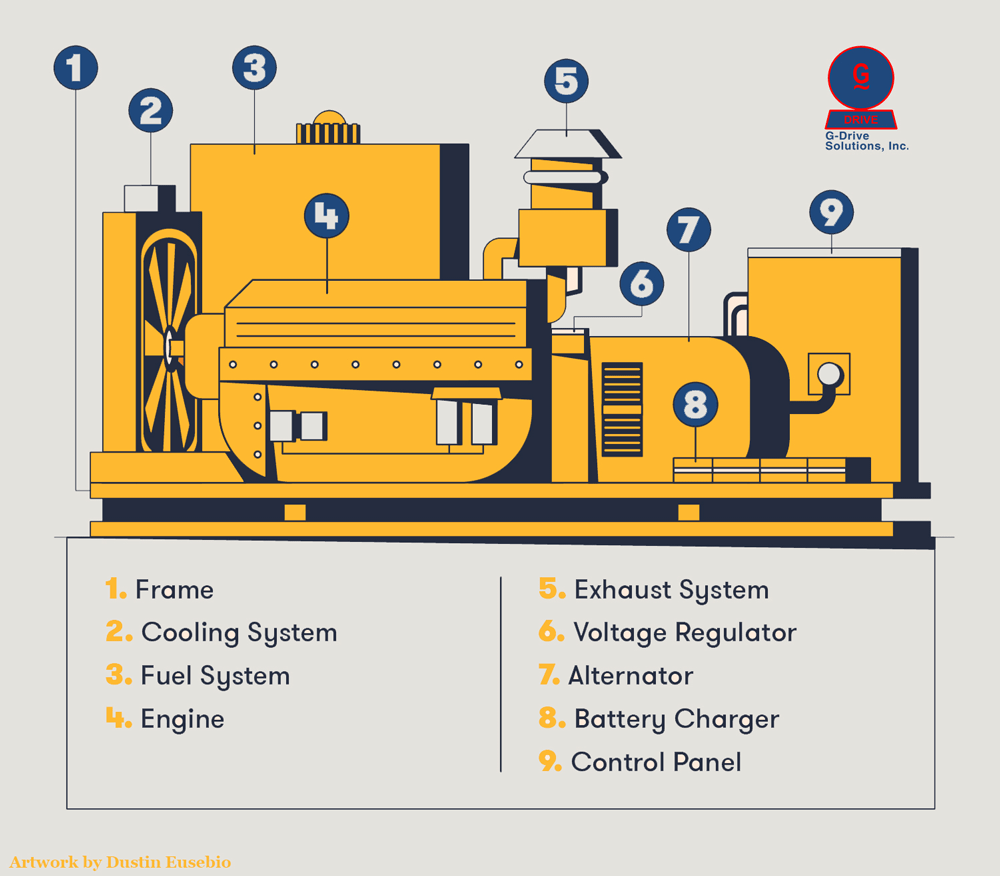
Most modern generators work thanks to a set of key components:
Frame: Supports all internal components and provides a protective structure for safer handling and transport.
Engine: Supplies mechanical energy for power generation. Engine size determines output. Engines run on diesel, gasoline, propane, or natural gas.
Alternator: Produces electricity via a rotor (rotating part) and stator (stationary part), generating alternating current (AC).
Fuel System: Supplies the generator with fuel from attached or external tanks, including supply and return lines.
Exhaust System: Safely routes toxic exhaust gases away from the generator and the environment.
Voltage Regulator: Maintains consistent voltage by converting AC current to the proper output level.
Battery Charger: Keeps the battery charged to start the engine reliably.
Control Panel: Provides external access to switches, gauges, and indicators, including start/stop functions, voltage settings, and engine metrics.
What Generators Are Used For
Generators serve both personal and commercial applications. They are most commonly used as backup power during brownouts or outages, but they can also provide primary power for off-grid construction sites or remote buildings.
Generators come in silent-type, open-type, or mobile/trailer configurations. Furthermore, many are connected to manual or automatic transfer switches for seamless grid-to-generator power transition. For detailed differences, see our Generator Types Guide.
How Generators Create Electricity: Step-by-Step
Fuel Combustion
The engine burns fuel (diesel, gasoline, propane, or natural gas) to generate mechanical energy.
Energy Transfer to Alternator
The engine drives the alternator, pushing electric charges through the wiring.
Magnetic Field Generation
As the rotor spins, it creates a magnetic field around the stator’s conductors.
Current Conversion
The moving magnetic field induces an electrical current, which the alternator converts into AC voltage.
Power Delivery
The resulting electricity is delivered to appliances, tools, or the building’s power system.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how does a generator work. Generators are essential for delivering electricity wherever and whenever it’s needed—during emergencies or in locations far from the grid. Understanding how generators work allows you to make smarter decisions when buying, using, or maintaining your unit.
Seeking a generator for your business or needing true 24/7 service? Contact G-Drive Solutions Inc., a leading provider of power generators Philippines, offering unmatched after-sales support and reliable backup solutions.