What are Microgrids?
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, microgrids are emerging as a pivotal solution for reliable, sustainable, and independent power. But what exactly is a microgrid? Simply put, a microgrid is a localized group of electricity sources and loads that typically operates connected to and synchronized with the traditional centralized grid (macrogrid), but can also disconnect and operate autonomously as an “island.” This ability to “island” provides critical resilience, ensuring continuous power supply even when the main grid experiences outages or disturbances.
Unlike the vast, interconnected macrogrid, a microgrid manages its own power generation, storage, and consumption. This localized control offers significant advantages, from enhancing energy security and reducing transmission losses to integrating renewable energy sources more effectively.
Key Characteristics of a Microgrid

-
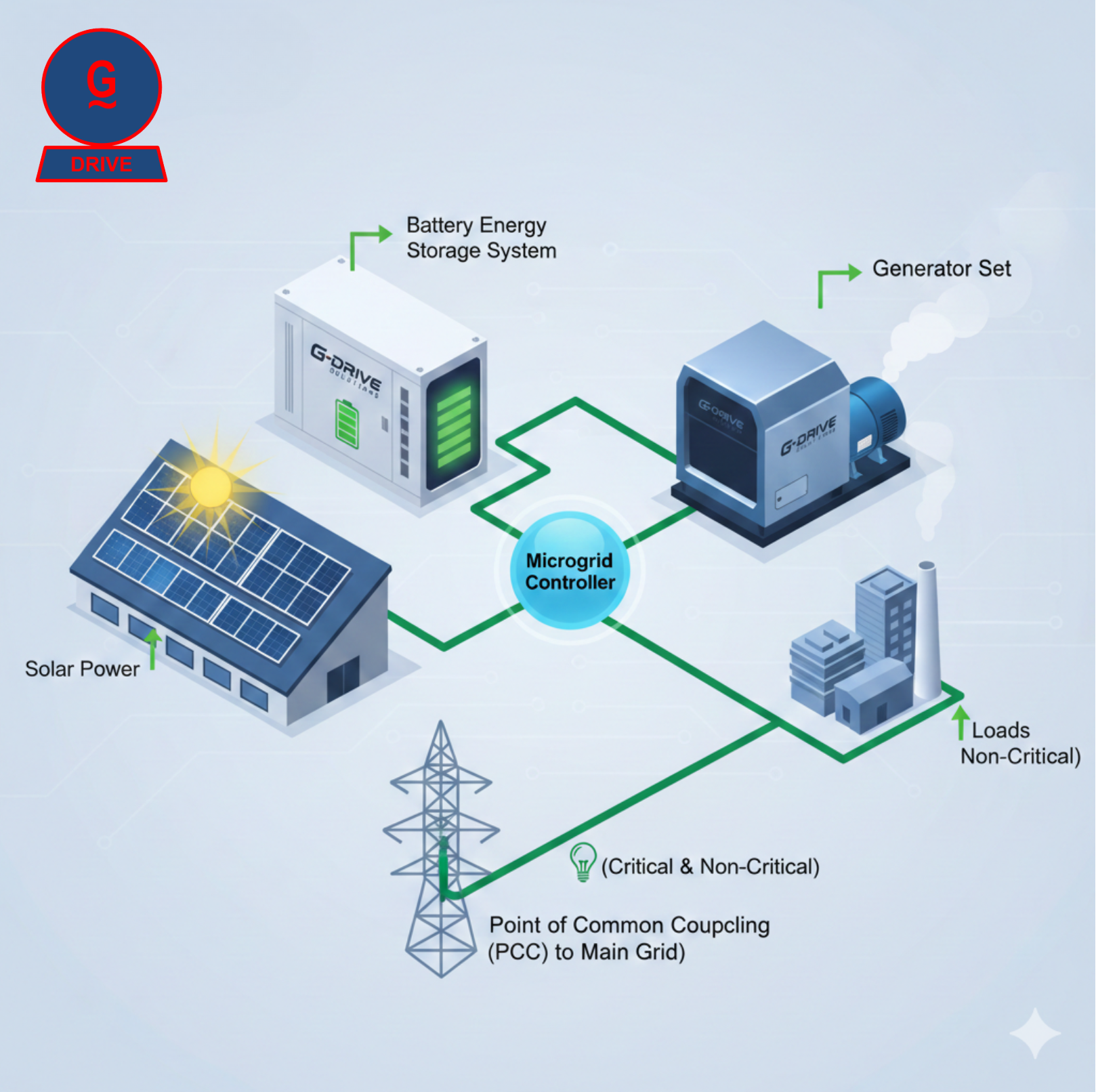
Defined Boundaries: A clear geographical and electrical boundary.
-
Local Generation: Power sources located within the microgrid.
-
Loads: Energy consumers within the microgrid.
-
Point of Common Coupling (PCC): The connection point to the main grid.
-
Advanced Control System: A sophisticated system that manages power flow, optimizes generation, and enables islanding capabilities.
The Essential Components of a Modern Microgrid
A robust microgrid thrives on a synergistic combination of diverse energy assets. While configurations can vary, the most common and effective modern microgrids integrate three core components: solar power, battery energy storage, and dependable generator sets.
Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are often the primary renewable energy source in many microgrids. They convert sunlight directly into electricity, offering a clean, sustainable, and increasingly cost-effective power generation option. The modular nature of solar panels allows for scalable installations, fitting a wide range of microgrid demands.
Battery Energy Storage Systems: The Power Buffer
Batteries are the backbone of microgrid stability, providing crucial energy storage. They capture excess solar energy generated during peak sunshine hours and discharge it when solar output is low (e.g., at night or on cloudy days), or when demand is high. This capability smooths out intermittent renewable generation, ensuring a consistent power supply and allowing the microgrid to maintain operation during grid outages.
Generator Sets: The Foundation of Reliable Power
While solar and batteries provide clean energy and storage, generator sets (gensets) play an indispensable role in ensuring the ultimate reliability and resilience of a microgrid. Often fueled by diesel, natural gas, or propane, these powerful units step in to provide power when renewable sources are insufficient or during extended grid outages.
Why Generator Sets Are Indispensable in Microgrids
Generator sets are not just backup power; they are a fundamental component that enhances the stability, security, and flexibility of modern microgrids.
Ensuring Continuous Power Supply
Renewable energy sources like solar are inherently intermittent. Clouds, nightfall, or seasonal variations directly impact their output. While batteries help bridge shorter gaps, they have finite capacity. This is where the generator set becomes critical. It provides on-demand, dispatchable power to seamlessly cover prolonged periods of low renewable generation or when battery reserves are depleted. This ensures that essential loads—and even non-essential ones—never lose power.
Black Start Capability
A crucial function of a generator set in a microgrid is its “black start” capability. If an entire microgrid experiences a total shutdown (a black out), the generator set can start independently without any external power source and then re-energize the entire system, including recharging batteries and bringing solar inverters back online. This capability is vital for rapid recovery after a major outage.
Grid Stabilization and Load Balancing
Microgrids require careful management of loads and generation to maintain stable voltage and frequency. Generator sets, with their robust and predictable output, can quickly respond to changes in demand or fluctuations in renewable generation. They act as a stable anchor, helping the microgrid controller balance the load and maintain power quality, which is crucial for sensitive equipment.
Economic Optimization
Beyond reliability, generator sets contribute to the economic efficiency of a microgrid. In certain scenarios, it might be more cost-effective to run a generator for a few hours during peak demand charges from the utility grid rather than drawing expensive power or depleting battery reserves too quickly. Intelligent microgrid controllers, like those supported by G-Drive Solutions technology, can optimize these operational decisions to minimize energy costs.
G-Drive Solutions: Powering Your Resilient Microgrid
At G-Drive Solutions, we understand the critical role that robust and reliable generator sets play in the success of any microgrid. We design and manufacture high-performance generator sets specifically engineered to integrate seamlessly with solar and battery storage systems, forming the cornerstone of your energy independence. Our advanced control systems and durable gensets ensure your microgrid operates at peak efficiency, providing uninterrupted power when it matters most.
Whether you are building a new microgrid or upgrading an existing system, G-Drive Solutions provides the dependable power generation assets that bring true resilience to your energy infrastructure. We are committed to fostering energy security and helping businesses and communities thrive with innovative power solutions.
Benefits of Embracing Microgrids
Adopting a microgrid strategy offers a multitude of advantages for various sectors, from industrial campuses to remote communities.
-
Enhanced Reliability: Microgrids provide continuous power, even when the main grid fails. This is crucial for critical infrastructure like hospitals, data centers, and military bases.
-
Improved Energy Security: By decentralizing power generation, microgrids reduce vulnerability to large-scale grid failures or attacks.
-
Cost Savings: Optimizing local generation and storage can reduce reliance on expensive grid power during peak times and lower transmission costs.
-
Sustainability: Microgrids facilitate greater integration of renewable energy sources, contributing to reduced carbon emissions.
-
Grid Support: When connected to the main grid, microgrids can provide ancillary services, such as voltage support and demand response.
Conclusion: Securing Your Energy Future with Microgrids
Microgrids represent a paradigm shift in how we generate, distribute, and consume electricity. By intelligently combining solar, battery storage, and the unwavering reliability of generator sets, they offer an unparalleled level of energy resilience and independence. For professionals and casual readers alike, understanding microgrids illuminates a path toward a more secure, sustainable, and robust energy future. As an integral component, the generator set ensures that this future remains consistently powered, no matter the external conditions.
#What are Microgrids?